-
Capabilities
-
Products and Services
-
About Us
-
Oil And Gas News
-
Oil and Gas Pipelines
-
Civil Projects
-
Process Units
-
Industrial Technology
-
Management Systems
-
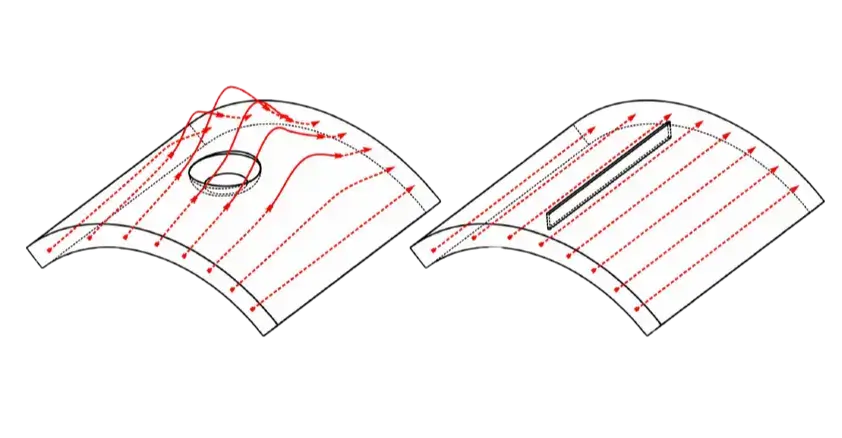
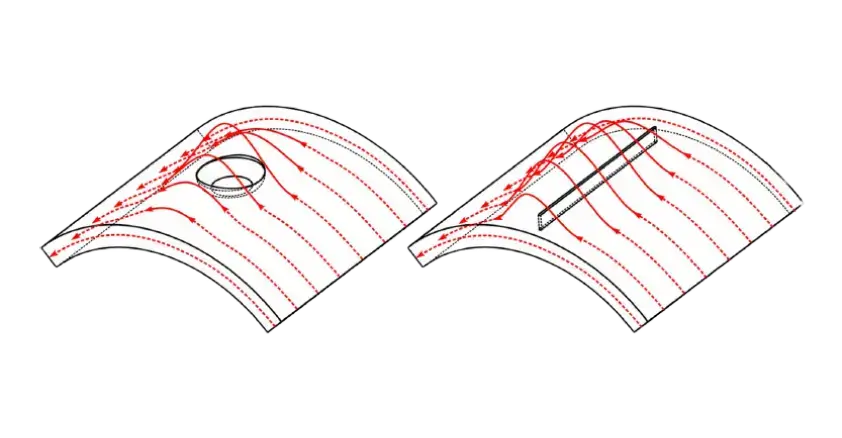
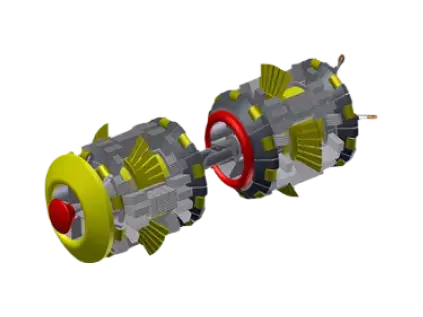
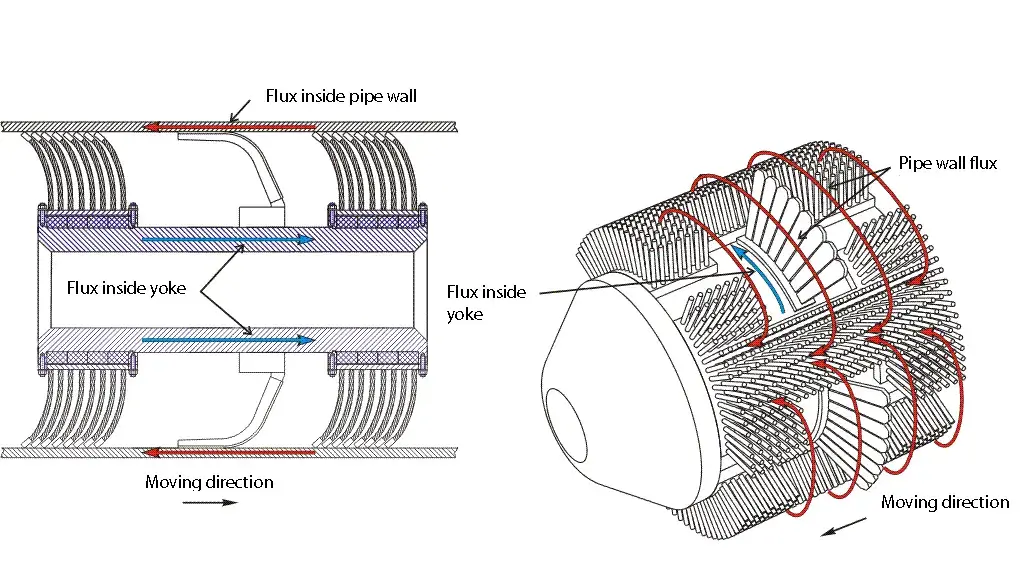
Inline Inspection
-
Unpigable Pipelines
-
Under Water Inspection-ROV
-
Cleaning Pigs
-
Repairing
-
Valve Clinic
-
Coating and Cathodic Protection
-
Fitness For Services(FFS) and Fitness For Purpose(FFP)
-
Leak Detection
-
Consultant and Project Management
- 2
- 2
- 2